Plastic tanks can be defined as containment vessels that are designed to store different kinds of substances. They are also commonly known as poly tanks, and are used in a variety of industrial applications. Read More…
Roto Dynamics Inc., custom rotational molders serving rotomolding and plastic tank needs nationwide. We are dedicated to our customers manufacturing needs. Building customer relationships based on integrity and communication assists us in developing a competitive advantage within the industry.

United States Plastic Corp. manufactures and distributes some 25,000 plastic items serving over 85,000 clients operating in a factory five acres under roof. Our major product is manufacturing plastic tanks, the distribution of bottles, carboy and plastic containers. This also includes plastic sheet, rods, tubes, flexible tubing and thousands of plastic fittings.

Sherman Roto Tank specializes in tanks that are manufactured to be suitable to store and process chemicals. Our tanks are a great choice for any industry. All our products go through extensive testing in order to surpass the industry standards. We offer sizes varying from 65 gallon to 800 gallon tanks. Along with tanks we manufacture customizable stands.
With over 100 years combined experience, All Plastics and Fiberglass has the experience to handle all your plastic and fiberglass needs.
Wagner Enterprise is a trusted leader in designing and manufacturing industrial tanks and mixers, providing reliable solutions for a wide range of industries. With a focus on innovation, quality, and customer satisfaction, we specialize in delivering custom-engineered tanks and mixers that meet the unique needs of our clients. Our comprehensive range of services includes tank design,...
Ryan Herco Flow Solutions is a leading national distributor for fluid handling products. Our family of products include; Plastic Tanks and storage containers, tubing and hose, process pipe and fittings, valves, pumps, filters and filter systems, instrumentation, flowmeters, sensors and corrosion resistant structural products. We have 29 U.S. Service Centers ready to serve you.
More Plastic Tank Companies
Comprehensive Guide to Plastic Tanks: Applications, Types, Materials, and More
Plastic tanks are essential solutions for safe, efficient, and cost-effective storage and transport of a wide range of substances. Whether you’re looking for plastic water tanks, chemical storage tanks, or custom rotationally molded tanks for industrial use, understanding the various options and considerations will help you choose the best plastic tank for your specific requirements. This guide explores everything you need to know about plastic tanks—from applications and materials to benefits, accessories, installation, and selection tips for buyers.
Applications
Plastic tanks serve a multitude of purposes in material storage, liquid containment, and transportation across diverse industries. Their corrosion resistance, lightweight nature, and adaptability make them the preferred choice for challenging and specialized storage needs. Below are some key industry applications:
- Agriculture: Used for water storage, irrigation, fertilizer mixing, pesticide and herbicide containment, and livestock watering systems. Plastic tanks help farmers manage resources efficiently and safely store agricultural chemicals.
- Petrochemical & Oil & Gas: Essential for the safe containment and transportation of petroleum, fuels, and chemicals. Plastic fuel tanks and plastic oil tanks offer robust chemical resistance and leak prevention.
- Water Treatment: Critical for potable water storage, rainwater collection, greywater systems, and wastewater processing. Plastic water tanks play a key role in municipal, commercial, and residential water management systems.
- Chemical Processing: Used for storing corrosive and reactive chemicals, including acids, alkalis, solvents, and industrial liquids. Plastic chemical tanks are designed for maximum chemical compatibility and safety.
- Food & Beverage: Food-grade plastic tanks ensure hygienic storage of ingredients, syrups, and beverages. They are easy to clean and meet FDA, NSF, and other regulatory standards.
- Recycling & Waste Management: Plastic tanks are widely utilized for collecting, storing, and transporting recyclable materials, hazardous waste, and leachate.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Used for storage of raw materials, process liquids, finished products, and for parts washing or electroplating baths.
- Fire Protection: Serve as critical reservoirs for fire suppression systems, emergency water supply, and sprinkler system storage.
- Residential & Commercial: Plastic tanks provide solutions for rainwater harvesting, septic systems, heating oil storage, and more.
Searching for the right plastic tank for your application?
Ask yourself: Will the tank be used for potable water, hazardous chemicals, fuel storage, or agricultural liquids? What capacity, shape, and installation environment do you need?
The History of Plastic Tanks
For millennia, humans have relied on tanks crafted from materials like stone, ceramic, and wood. The Indus Valley Civilization, flourishing from 3000 to 1500 BC, employed tanks to store water and grain. Similarly, medieval Europeans fortified their castles with water tanks as provisions during sieges.
Plastic tanks emerged significantly only from the mid-20th century onwards. While plastic was synthesized from the 1800s, it couldn’t be effectively utilized for tank production until advancements in technology occurred. The breakthrough arrived in the 1960s with the development of rotational plastic molding, enabling manufacturers to create large hollow containers initially using low-density polyethylene. Over the past five decades, continuous advancements by engineers and chemists have refined processes and introduced new plastic compounds. This ongoing innovation has fostered growth and diversification within the plastic tank industry.
Plastic tank manufacturers and suppliers are increasingly focusing on sustainability. While plastic tanks are recyclable, the industry continues to explore ways to reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a healthier planet. Initiatives such as using recycled plastics, developing biodegradable polymers, and establishing tank recycling programs are gaining traction, making plastic tanks a more eco-friendly choice for modern storage needs.
Are you interested in the evolution of plastic tanks and how modern manufacturing innovations can impact your storage solutions? Explore top manufacturers who are leading the way in sustainable plastic tank production.
Design
Production
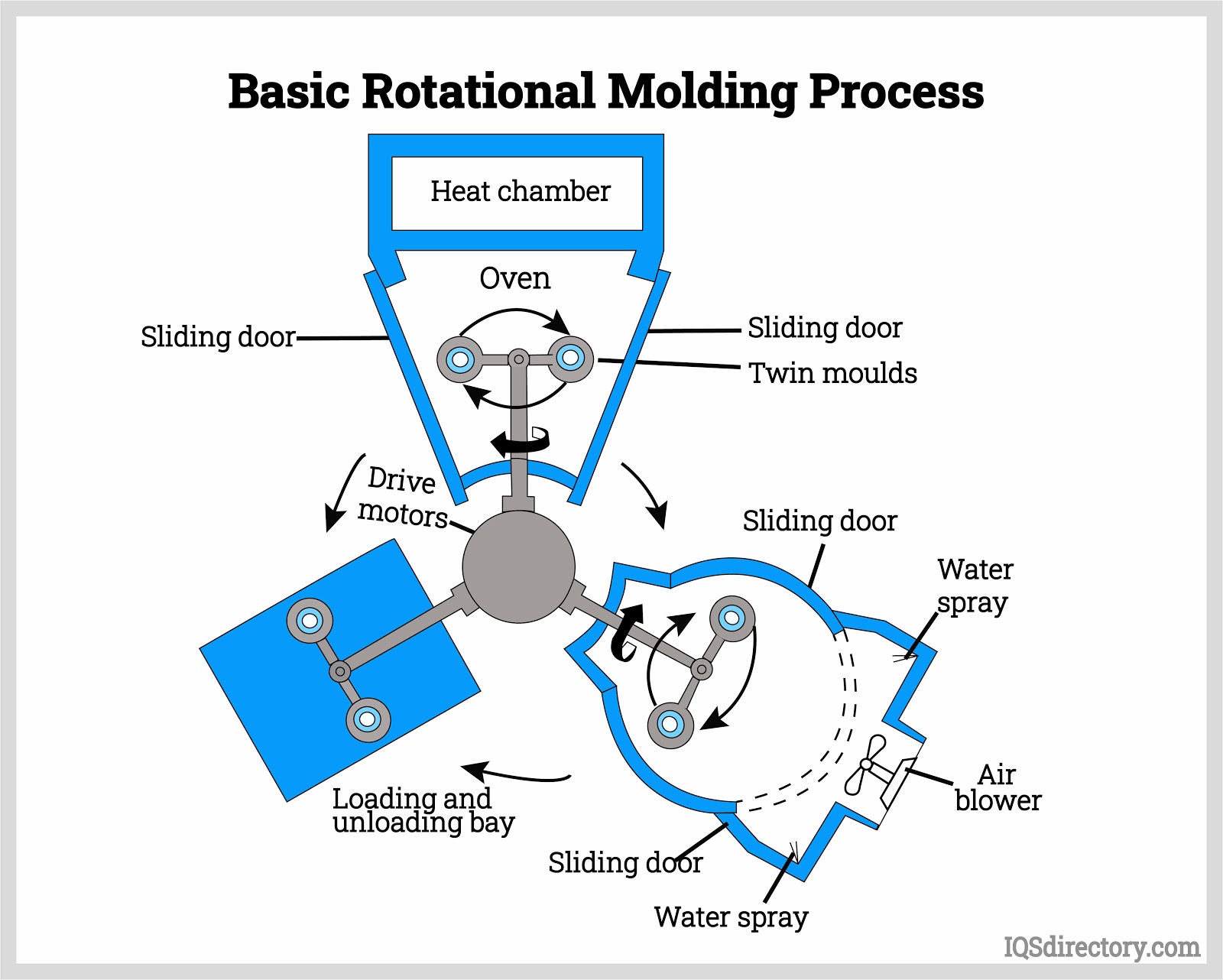
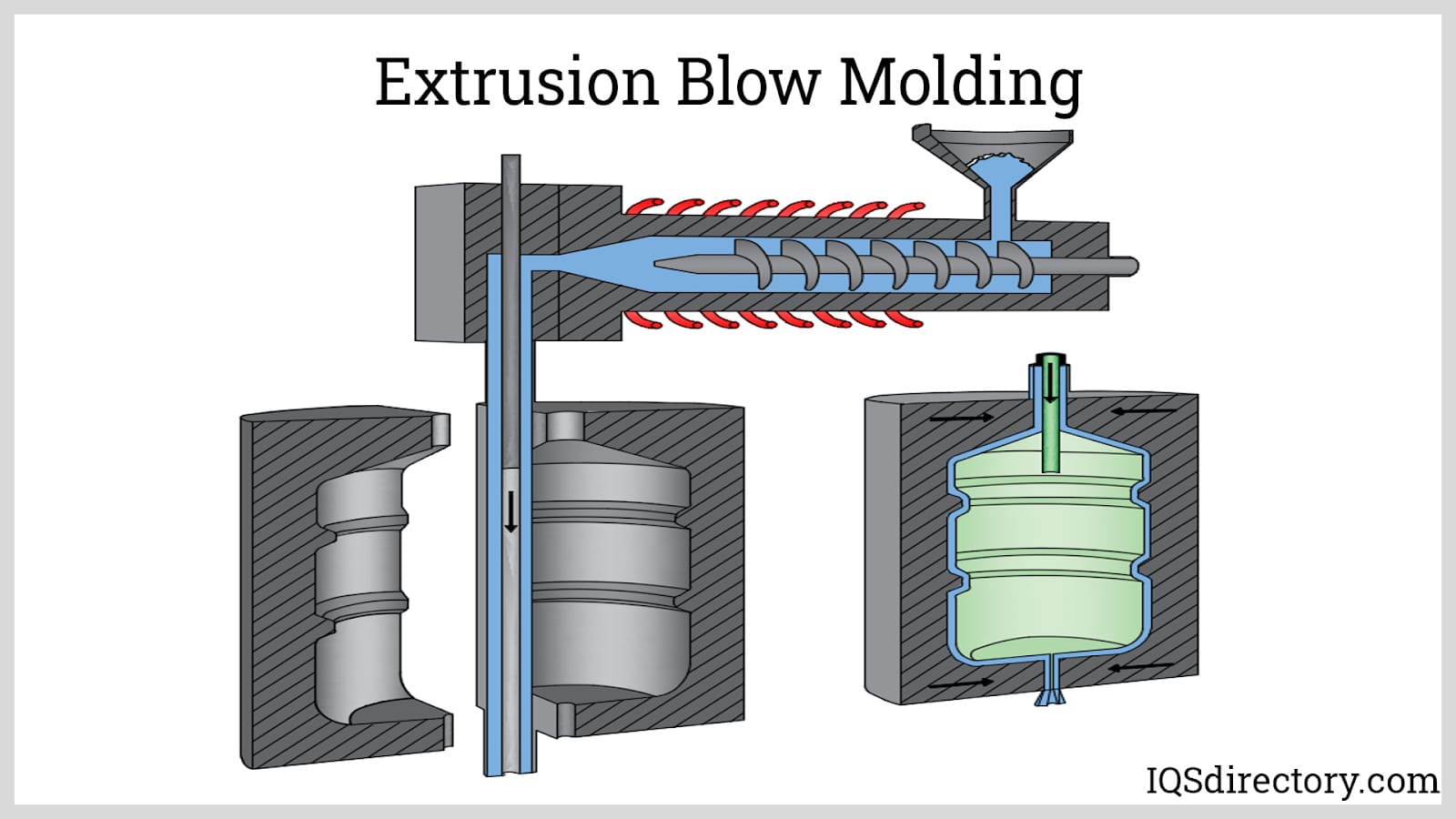
Plastic tank manufacturing typically utilizes two key processes: rotational molding (rotomolding) and plastic injection molding. The process begins with the creation of a stainless steel or aluminum mold, digitally designed to precise specifications. The mold is filled with plastic granules or powder—most often polyethylene or polypropylene—and is then sealed and rotated over a heat source. As the mold spins, the plastic melts and coats the interior, forming a seamless, hollow vessel. After cooling and solidification, the finished tank is removed.
Rotational molding is especially popular for producing large, seamless, stress-free tanks, while injection molding is often used for smaller, more complex shapes. The wall thickness of the tank can be adjusted by varying the amount of plastic used, ensuring structural integrity and durability tailored to the tank’s application.
For buyers seeking custom plastic tanks, advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D modeling enable precise customization to meet unique requirements. This includes specialized fittings, baffles, flanges, and ports, facilitating seamless integration into any system.
Materials
Plastic tanks are typically made from materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP). Polyethylene is the most commonly used due to its chemical resistance, affordability, and flexibility. Key grades of polyethylene utilized include:
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Known for strength, chemical resistance, and suitability for industrial and chemical storage tanks.
- Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE): Offers flexibility and is used for tanks where impact resistance is needed.
- Medium Density Polyethylene (MDPE): Balances toughness and chemical compatibility.
- Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE): Provides enhanced crack resistance and flexibility.
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE): Offers superior durability and resistance to stress cracking, ideal for aggressive chemicals.
Additional plastics like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are used for specialized chemical storage where higher temperature or abrasion resistance is required. The choice of material affects the tank’s performance in terms of:
- Corrosion resistance
- Impact resistance
- Chemical compatibility
- UV resistance
- Temperature tolerance
- Durability and longevity
- Food-grade safety (where applicable)
Still deciding which plastic tank material is right for your application? Contact a tank specialist or compare manufacturers to discuss your chemical compatibility and durability requirements.
Customization
If you can’t find the tank you need on the standard market, opting for custom manufacturing might be your best bet. Custom plastic tanks come in a variety of configurations, orientations (horizontal or vertical), colors, shapes, and sizes to suit your specific needs. Manufacturers can even incorporate translucent walls, allowing for easy monitoring of tank contents. Plastic tanks are available in sizes ranging from 15 gallons to 16,000 gallons, ensuring they meet diverse capacity requirements. Optional features include molded-in fittings, manways, ladder attachments, and baffles for mixing or sloshing control.
Wondering how to get a quote for a custom plastic tank? Consider your storage volume, required certifications, installation site, and whether you need accessories like pumps or level gauges.
Types
Plastic tanks can be categorized in several ways, with three primary methods being most common:
- Based on the material they contain.
- According to the type of material used in their fabrication.
- Considering their application and design.
Various types of plastic tanks are categorized based on the substances they store. These include water tanks, plastic fuel tanks, chemical tanks, and plastic oil tanks. Examples of tanks categorized by their material composition include polyethylene tanks, polypropylene tanks, and FRP tanks. Additionally, common examples in the third category comprise septic tanks, storage tanks, double wall tanks, and cone bottom tanks.
Water Tank
The plastic water tank serves a specific purpose: storing water for various applications such as household drinking, fire extinguishing, irrigation, and emergency reserve. Plastic water tanks can be made from several materials, with PE being the most prevalent. PP, PVC, and PVDF are also options for fabrication. PE is favored due to its lightweight properties, UV stability, and resistance to chemicals. Water tanks intended for human consumption must meet food-grade standards (such as NSF/ANSI 61).
Looking for a large capacity water storage solution for your property or facility? Explore top-rated water tank options and compare features such as capacity, fittings, and installation requirements.
Plastic Fuel Tank
Plastic fuel tanks serve dual roles in transporting and storing flammable substances while gauging substance levels in the engine, proving indispensable for anticipating potentially hazardous situations. They are typically crafted from five primary materials: high-density polyethylene (HDPE), PP, recycled polyethylene (regrind plastic), and a plastic adhesive or ethyl vinyl alcohol (EVOH). Modern fuel tanks are designed to meet rigorous EPA and DOT standards for fuel containment, vapor control, and crash safety, making them ideal for automotive, marine, and industrial use.
How do you choose the right plastic fuel tank? Consider the fuel type, required certifications, tank shape, and whether impact or vibration resistance is critical for your application.
Chemical Tank
Chemical tanks are engineered to store aggressive or highly reactive chemicals, like sulphuric acid, sodium hypochlorite, or industrial solvents. Manufacturers construct these chemical storage tanks with interiors and fittings designed to resist chemical reactions, corrosion, and permeation. Features such as double-wall containment, venting systems, and chemical-resistant gaskets are often included to maximize safety and regulatory compliance.
Not sure which chemical storage tank is right for your facility? Contact a chemical tank supplier and request a compatibility chart or engineering consultation.
Plastic Oil Tank
Plastic oil tanks resemble plastic fuel tanks, but they are crafted from distinct materials. Manufacturers typically use fiberglass reinforced plastic (also known as glass reinforced plastic or FRP) and molded polyethylene to fabricate them. These tanks are used for residential heating oil, industrial lubricants, and waste oil storage, offering corrosion resistance and long service life versus steel alternatives.
Polyethylene Tank
Polyethylene tanks exhibit versatility, serving non-pressure storage needs for a wide array of liquids, chemicals, and solids such as alkalis, acids, water, and solvents. These tanks are fortified with UV treatment for exceptional durability and are food grade approved, ensuring suitability for storing water and consumables. Polyethylene is a top choice for rotational molding due to its strength and flexibility, and it is widely used for agricultural, municipal, and industrial tank applications.
Polypropylene Tank
Polypropylene tanks boast resistance to heat (with a melting point of 320℉), moisture, chemicals, and corrosive materials. They are known for their durability, lightweight nature, and rigidity. These qualities make them particularly favored in stainless steel processing plants, electroplating operations, and environments where high thermal or chemical resistance is required.
FRP Tank (GRP Tank)
FRP tanks, primarily composed of glass-reinforced plastic (GRP), are widely employed in food processing due to their FDA approval. These tanks offer excellent structural strength, temperature resistance, and protection against chemical attack, making them ideal for demanding industrial and municipal applications.
Septic Tank
Septic tanks serve a highly specialized role, designed specifically to contain substances integral to sewage treatment processes. A plastic septic tank system comprises two fundamental components: the septic tank and a drain field, working in tandem to form an on-site sewage treatment system. Plastic septic tanks are lightweight, easy to install, and less prone to corrosion than concrete or steel alternatives.
Storage Tank
Plastic storage tanks serve the basic function of storing various materials—liquids, solids, or slurries. This versatile application finds use across nearly every industry, showcasing its broad utility. Consequently, these tanks come in a myriad of configurations tailored to different needs, from vertical upright tanks to horizontal leg tanks and specialty containment tanks.
Double Wall Tank
Double-wall tanks are characterized by an outer layer fortified with an additional plastic coating, from which the tank derives its name. This supplementary plastic layer enhances safety by effectively averting leaks during material storage, transportation, and rigorous processing. Hence, double-wall tanks are employed for the containment of hazardous waste and other substances that pose potential risks. Many environmental regulations require double-wall containment for chemicals and fuels to prevent soil and groundwater contamination.
Cone Bottom Tank
Cone bottom tanks derive their name from their tapered, conical bottom end. They aim to achieve two main objectives: 1) streamline the dispensing process from the tank’s base, and 2) enhance the efficiency of draining the tank. Cone bottom tanks are ideal for applications where complete discharge of contents is vital, such as in chemical mixing, food processing, brewing, and wastewater treatment.
Need help choosing the best tank design? Compare tank types or request recommendations from reputable plastic tank suppliers.
Advantages of Plastic Tanks
There are numerous advantages to opting for plastic tanks over other alternatives, such as metal, concrete, or fiberglass tanks. Here are some of the top benefits:
- Chemical and corrosion resistance: Plastic is less prone to react with the contents compared to materials like metals, making it ideal for aggressive chemicals and sensitive applications.
- Lightweight and easy handling: Plastic tanks are significantly lighter than steel or concrete tanks, reducing transportation and installation costs.
- Seamless, leak-resistant construction: Rotationally molded plastic tanks are typically seamless, minimizing the risk of leaks or weak points.
- Design versatility: Plastic tanks can be custom-molded into various shapes, sizes, and colors, with options for vertical, horizontal, and specialty tank designs.
- Cost-effective: Plastic tanks offer excellent value, with lower up-front and maintenance costs than many alternative materials.
- Recyclable and reusable: Most plastic tanks can either be recycled or repurposed for secondary uses, supporting sustainability and waste reduction goals.
- Precision manufacturing: Plastic tanks are manufactured with uniform wall thickness and consistent quality, ensuring reliable performance.
- Long service life: With proper care and installation, plastic tanks can deliver decades of dependable use.
Curious about the cost savings and environmental benefits of switching to plastic tanks? Contact a supplier for detailed comparisons with traditional tank materials.
Accessories
Depending on the type of tank and its intended use, investing in plastic tank accessories can greatly enhance functionality, safety, and convenience. Popular accessories and add-ons include:
- Fittings and adapters: For connecting hoses, pipes, or pumps to the tank.
- Valves: Essential for regulating water or fluid flow in storage, dispensing, or mixing applications.
- Hoses and tubing: For transferring liquids to and from the tank. Explore plastic tubing solutions for compatible options.
- Tie-down kits and restraints: To secure tanks during transport or to withstand wind and seismic activity.
- Pumps: Electric or manual pumps for efficient liquid transfer.
- Rainwater collection adaptors: For harvesting and storing rainwater safely.
- Lids, manways, and covers: For safe access and protection against contamination.
- Precision gauges: For monitoring fluid levels and tank capacity.
- Siphon tubes, strainer baskets, and float valves: For specialized dispensing, filtration, or automatic shutoff.
Want to customize your plastic tank system? Ask a supplier which accessories are compatible with your chosen tank model and application.
Installation
Proper installation of your plastic tank is vital for safety, durability, and optimal performance. Installation procedures vary by the details of the installation site, such as whether it is above or below ground, indoor or outdoor, and by the tank’s application. For example, do you require easy access to the contents? That impacts where you place your tank.
Key installation considerations include:
- Ensuring the tank is supported from the bottom—never suspend a tank by its fittings.
- Mounting on a stable, level, and load-bearing surface (such as a concrete pad or compacted gravel base).
- Providing adequate clearance for inspection, maintenance, and filling operations.
- Using appropriate tools and following the manufacturer’s detailed installation instructions to avoid damage.
- Securing tanks with tie-downs or restraints in seismic or high-wind areas.
- Following all local codes and environmental regulations, particularly for underground or hazardous material storage.
For expert guidance, consulting your supplier is highly recommended for comprehensive advice. Many manufacturers also offer on-site installation services or can connect you with certified installers to ensure compliance and long-term reliability.
Need help with plastic tank installation? Request an installation guide or find a certified installer through your supplier.
Proper Care for Plastic Tanks
With the right care and maintenance, plastic tanks can provide years of reliable service. Here are a couple of tips to ensure plastic tanks endure over time if cared for properly:
- Always ensure the tank is supported from the bottom when handling.
- Make sure to always install or mount the tank on a stable surface capable of handling the pressure to prevent the risk of it tipping over and rupturing.
- Ensure materials prone to falling are kept away from the tank.
- Avoid exposing your tank to extreme temperatures, whether excessively hot (including hot water) or excessively cold.
- Similarly, avoid placing your tank in environments that it isn’t designed to handle (e.g., harsh chemicals or UV exposure without protection).
- Avoid storing tanks containing flammable liquids near any open flames.
- Regularly clean the tanks after each use to prevent buildup, contamination, or microbial growth.
Looking for tank care products or maintenance tips? Browse our resources or connect with a tank specialist for personalized support.
Standards
Your plastic tank must meet specific industry standards and certifications tailored to your application, industry, and location. In the United States, for instance, tanks intended for petroleum storage must conform to the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards. Similarly, tanks holding flammable liquids should comply with guidelines from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). Other essential standards are established by organizations such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL), the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). These standards serve as critical benchmarks used across governmental regulations and various industries.
For food and potable water storage, look for NSF/ANSI 61 or FDA compliance. Some tanks may also require ISO certification or European CE marking for international use.
Unsure which certifications your tank needs? Request compliance documentation from your supplier or consult with an industry expert to ensure you meet all safety and regulatory requirements.
Selecting a Manufacturer
Before committing to collaborate with any supplier or manufacturer, ensure they can meet your specifications and uphold a reputation for outstanding customer service. When evaluating plastic tank manufacturers, consider the following:
- Proven experience and expertise in your industry.
- Ability to provide custom solutions tailored to your requirements.
- Compliance with all relevant standards and certifications.
- Comprehensive post-sales support, warranty, and installation services.
- Positive reviews and references from similar customers.
For reliable manufacturers, explore the companies featured on this page. Each partner we endorse has demonstrated expertise in their field. Dive deeper into their profiles and visit their respective websites to learn more about them. Comparing quotes, technical support, and warranty terms will help you make an informed decision and ensure your investment delivers lasting value.
Ready to request a quote, schedule a consultation, or compare top plastic tank manufacturers? Start your search here for the best suppliers in your region.
For related storage and fluid management solutions, check out our Plastic Tubing website and our Rotational Molding website for a wide range of compatible products.
Still have questions about plastic tanks, materials, or installation?
Browse our FAQs, request a product catalog, or speak with an expert today to find the perfect plastic tank solution for your unique needs!
What are the main applications of plastic tanks?
Plastic tanks are used across numerous industries for applications such as water storage, chemical processing, agriculture (fertilizer and pesticide storage), petrochemical containment, food and beverage ingredient storage, water treatment, recycling, fire protection systems, and residential needs like rainwater harvesting and septic systems.
What are the most common materials used to manufacture plastic tanks?
The most common materials used for plastic tanks are polyethylene (including HDPE, LDPE, MDPE, LLDPE, XLPE), polypropylene, fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). The choice of material impacts chemical resistance, durability, temperature tolerance, and suitability for food-grade applications.
What are the key advantages of plastic tanks over metal or concrete tanks?
Plastic tanks offer advantages including high chemical and corrosion resistance, lightweight and easy handling, seamless leak-resistant construction, broad design versatility, cost savings, recyclability, precise manufacturing quality, and long service life with proper care.
How are plastic tanks manufactured?
Plastic tanks are typically made using rotational molding (rotomolding), which forms seamless, hollow vessels by heating and rotating a mold filled with plastic powder. Injection molding is used for smaller or more complex shapes. Advanced manufacturing may use CAD and 3D modeling for custom designs and fittings.
What types of plastic tanks are available?
There are many plastic tank types, including water tanks, chemical tanks, plastic fuel tanks, oil tanks, polyethylene and polypropylene tanks, FRP (GRP) tanks, septic tanks, storage tanks, double-wall tanks, and cone bottom tanks. Each type is suited for specific storage or process needs and applications.
What accessories can be added to plastic tanks?
Plastic tank accessories include fittings, adapters, valves, hoses or tubing, tie-down kits, pumps, rainwater collection adaptors, lids and covers, precision gauges, siphon tubes, strainer baskets, and float valves. These enhance convenience, safety, and system integration.
How should I care for and maintain my plastic tank?
To ensure long service life, always support the tank from the bottom, install it on a stable, load-bearing surface, keep it away from falling objects and extreme temperatures, avoid flammable storage near open flames, regularly clean the tank, and use it only for suitable contents.
What industry standards and certifications should my plastic tank meet?
Plastic tanks may need to comply with standards from the American Petroleum Institute (API), National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), Underwriters Laboratories (UL), ANSI, ASME, ASTM, NSF/ANSI 61, and FDA. Some tanks also require ISO or CE certification, depending on the application and location.






 55 Gallon Drums
55 Gallon Drums Floor Gratings
Floor Gratings Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Plastic Containers
Plastic Containers Plastic Pallets
Plastic Pallets Plastic Tanks
Plastic Tanks Steel Shelving
Steel Shelving Stainless Steel Tanks
Stainless Steel Tanks Storage Racks
Storage Racks Work Benches
Work Benches Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services